|
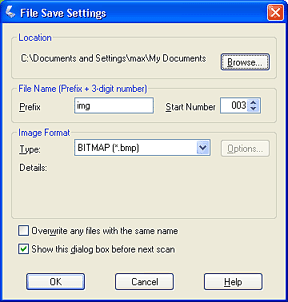
Format
(File Extension)
|
Explanation
|
|
BITMAP (*.BMP) (Windows only)
|
Standard image file format used in Windows. Most Windows application including word processing application can read and prepare images in this format.
|
|
PICT (*.PCT) (Macintosh only)
|
Standard image file format for the Macintosh. Almost all of the software applications for the Macintosh (such as word processing software) support the PICT file format.
|
|
JPEG (*.JPG)
|
Compressed file format. The compression quality can be selected; the JEPG format enables relatively high compression ratio. However, the higher the compression ratio is, the lower the image quality becomes. (Note that the original data cannot be restored.) In addition, the quality deteriorates every time the data is saved. The TIFF format is recommended in cases where modification, retouch and the like are required.
|
|
TIFF (*.TIF)
|
File format created for exchanging data among many applications such as graphic and DTP software. When scanning black & white images, you can specify the compression type.
|
|
Multi-TIFF (*.TIF)
|
TIFF format where multiple pages are saved to the same file, When you scan documents using the Automatic Document Feeder, they all stored in the same file. (With other formats, each document is saved in a separate file.) However, to open the Multi-TIFF files, you need an application supporting this format.
|
|
PDF (*.PDF)
|
PDF is a document format that is independent of platforms. To use PDF documents, you need Adobe Acrobat® Reader® or Acrobat. When you save color or grayscale images in PDF, you can select a compression quality.
|