How To
To save scanned images without editing them in an application, start EPSON Scan directly. After scanning images, the scanned images are automatically saved as files in the folder specified in the File Save Settings dialog box. This operation can be set up as follows:
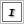 | Open the File Save Settings dialog box. |
For Windows users:
Click Start, point to All Programs (for Windows XP users) or Programs (for Windows Me, 98, or 2000 users), point to EPSON Scan, and then select EPSON Scan.
For Mac OS 9 users:
Select EPSON Scan from the Apple menu.
For Mac OS X users:
Click the EPSON Scan icon in the Applications folder.
| Note: |
|
 | Specify a location where scanned images are saved. If you want to change the default location, click Browse (for Windows) or Choose (for Macintosh) and then select a desired folder. |
 | Specify a file name with an alphanumeric character string (prefix) and a 3-digit number (start number). |
If you want to change the file name, type an alphanumeric character string in Prefix and select a start number. The name of a file is generated using a combination of the prefix and number specified here.
| Note: |
|
|
|
 | Select a file format from the following table. Depending on the selected file format, the Options button may be available so that you can make detailed settings for scanned images. |
|
Format |
Explanation |
|
BITMAP (*.BMP) (Windows only) |
A standard image file format for Windows. Most Windows applications including word processing applications can read and prepare images in this format. |
|
JPEG (*.JPG) |
A compressed file format. The compression quality can be selected. The JEPG format enables relatively high compression ratio. However, the higher the compression ratio is, the lower the image quality becomes. (Note that the original data cannot be restored.) In addition, the quality deteriorates every time the data is saved. The TIFF format is recommended in cases where modification, retouch and like are required. |
|
Multi-TIFF (*.TIF) |
A TIFF format where multiple pages are saved to the same file. When you scan documents using the Automatic Document Feeder, they are all stored in the same file. (With other formats, each document is saved in a separate file.) However, to open the Multi-TIFF files, you need an application supporting this format. |
|
PDF (*.PDF) |
A document format that is independent of platforms. To use PDF documents, you need Adobe Acrobat® Reader® or Acrobat. When you scan documents using the Automatic Document Feeder, multiple pages are saved to a single file. When you save color or grayscale images in PDF, you can select a compression quality. |
|
PICT (*.PCT) (Macintosh only) |
A standard image file format for Macintosh. Most Macintosh applications including word processing applications can read and prepare images in this format. |
|
TIFF (*.TIF) |
A file format created for exchanging data among many applications, such as graphic and DTP software. When scanning black & white images, you can specify the compression type. |
 | Click OK. |
EPSON Scan starts scanning.
 | The scanned image is automatically saved in the specified location. |
If the Open image folder after scanning check box in the File Save Settings dialog box is selected, Windows Explorer (Windows) or Finder (Macintosh) automatically opens the folder where the scanned image is saved when EPSON Scan finishes scanning.
 Previous |
 Next |